Financial planning is often seen as an essential step for individuals looking to achieve financial stability and long-term success. It is a holistic process that involves reviewing your entire financial situation, identifying your goals, and creating a plan to manage your money effectively in order to meet those goals. The ultimate aim of financial planning is to help you prepare for future needs, such as retirement, education, homeownership, and estate planning, while ensuring that your financial decisions are aligned with your overall life priorities.
Let’s break down what financial planning entails, why it matters, and how it can benefit you.
1. The Purpose and Definition of Financial Planning
At its core, financial planning is the process of evaluating your current financial situation and creating a roadmap to achieve your long-term goals. This goes beyond simply managing daily expenses or tracking your savings. It is about building a strategy that takes into account your present and future needs, helping you make informed decisions that will improve your financial wellbeing over time.
Financial planning helps individuals address a wide range of financial concerns, from budgeting and debt management to saving for retirement or education. It’s a dynamic process that can be revisited as your life circumstances change, such as when you get married, have children, or retire. The key goal is to create a comprehensive strategy that ensures your finances are aligned with your broader life objectives, providing you with a sense of financial security and peace of mind.
In short, financial planning is not just about accumulating wealth—it’s about making the best use of your resources to support the life you want to live.
2. The Broad Scope of Financial Planning
One of the misconceptions about financial planning is that it’s only about investments. While investment management is an important component, financial planning covers much more. A good financial plan takes into account many facets of your financial life, each of which contributes to your overall financial health.
Some of the key areas that financial planning addresses include:
- Budgeting and Cash Flow Management: This is about tracking your income and expenses to ensure you are living within your means. Budgeting helps you prioritize saving, managing debt, and planning for both short-term and long-term needs.
- Insurance Planning: Protecting yourself and your family from financial hardship is essential. Insurance planning may involve evaluating your need for life insurance, health insurance, disability insurance, and other forms of coverage that safeguard your assets and income.
- Retirement Planning: Building a plan to ensure you have enough money to live comfortably in retirement is one of the most common reasons people seek financial planning advice. This includes choosing retirement accounts, like 401(k)s or IRAs, and strategizing how much to save each year.
- Tax Planning: Financial planning also involves tax optimization strategies. By working with a financial planner, you can identify ways to minimize your tax burden, which may include tax-advantaged savings accounts or tax-loss harvesting strategies.
- Estate Planning: This is about preparing for the distribution of your wealth after your death. Estate planning involves creating a will, establishing trusts, and planning for potential estate taxes.
- Education Funding: Many individuals want to plan for their children’s or grandchildren’s education. This could involve setting up a 529 plan or other savings vehicles designed to grow over time and meet the cost of tuition and related expenses.
Each of these areas is interconnected, and a well-rounded financial plan will take all of them into account to create a cohesive strategy.
3. The Role of a Financial Planner
While some individuals are capable of creating their own financial plans, many people turn to professionals for help. A financial planner is a licensed professional who specializes in assessing your financial situation and helping you design a personalized plan that aligns with your goals. Financial planners can help you evaluate your current financial status, including income, assets, and liabilities, and use that information to create a roadmap for achieving your financial objectives.
Financial planners offer a variety of services, depending on their expertise and certifications. The most widely recognized certification for financial planners is the Certified Financial Planner (CFP®) designation. Planners with this certification are required to pass rigorous exams and adhere to ethical standards, ensuring that they have the knowledge and skills necessary to provide comprehensive advice.
Some planners work on a fee-only basis, meaning they do not receive commissions from selling financial products. This can help reduce potential conflicts of interest. Others may work on a commission basis, particularly those who sell insurance or investment products. Understanding how your financial planner is compensated is crucial to determining whether their recommendations are truly in your best interest.
The services offered by a financial planner can range from creating a one-time financial plan to providing ongoing guidance and portfolio management. For individuals with complex financial situations, a financial planner may offer continuous support, helping them adjust their plan as circumstances change.
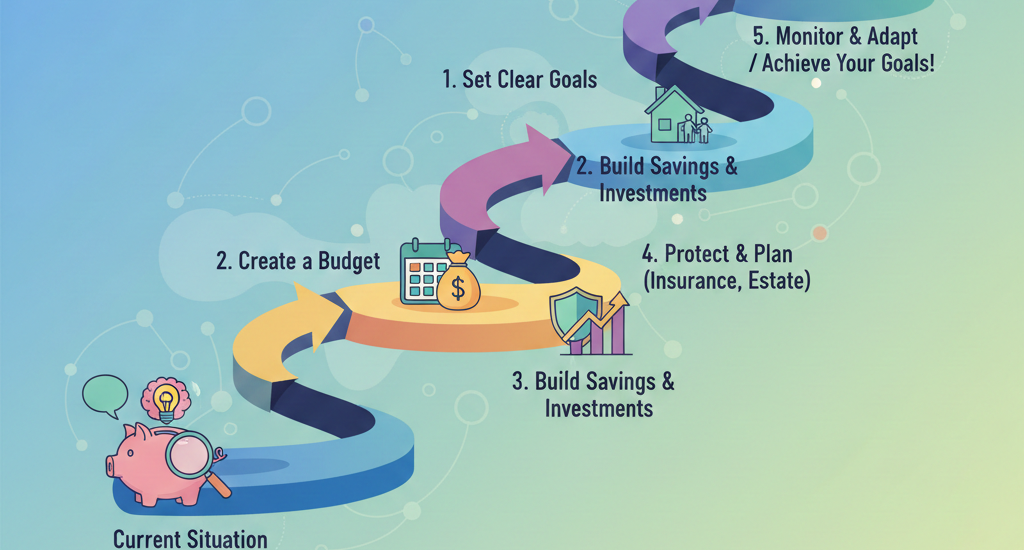
4. The Process of Creating a Financial Plan
Creating a financial plan is a structured process that typically follows several key steps:
Step 1: Assessing Your Current Financial Situation
The first step in creating a financial plan is to take stock of your current financial situation. This includes reviewing your income, expenses, debts, assets, and liabilities. A comprehensive assessment will also include identifying areas of strength and weakness, as well as any potential risks that could affect your future financial stability.
Step 2: Setting Financial Goals
Once you have a clear picture of where you currently stand, the next step is to define your financial goals. These could include short-term goals, such as building an emergency fund, and long-term goals, such as saving for retirement or purchasing a home. Clearly defined goals will help you create a focused and actionable plan.
Step 3: Developing a Strategy
After defining your goals, the next step is to create a plan to reach them. This may involve strategies for saving, investing, paying off debt, or reducing expenses. Your financial planner can help you determine the best course of action to achieve your goals within the timeline you’ve set.
Step 4: Implementation
Once your plan is in place, it’s time to take action. This step may involve setting up retirement accounts, creating a budget, buying insurance, or beginning an investment strategy. Your financial planner can assist with implementing these strategies and ensuring you stay on track.
Step 5: Monitoring and Reviewing Your Plan
Financial planning is an ongoing process. It’s important to regularly review and adjust your plan to ensure it remains aligned with your goals and adapts to any changes in your life. A good financial planner will help you track your progress and make adjustments as needed, whether that means reallocating investments, changing insurance policies, or altering your savings goals.
5. The Cost of Financial Planning
The cost of financial planning varies significantly based on the services provided and the advisor’s compensation structure. Some financial planners charge an hourly rate, while others may work on a retainer basis or receive commissions for selling financial products.
A flat fee for a comprehensive financial plan can range from several hundred dollars to a few thousand, depending on the complexity of your situation. A more common approach is a fee-based model, where the planner charges a percentage of the assets they manage, typically ranging from 0.5% to 1% per year.
For individuals looking for a standalone financial plan (without ongoing management), surveys indicate that the average cost for a financial plan can be around $2,000 to $3,000. However, this can vary depending on the advisor’s reputation and the amount of work involved.
While hiring a financial planner involves a cost, many individuals find that the value of professional advice far outweighs the expense, particularly when it comes to achieving long-term financial security.
6. Choosing the Right Financial Planner
When choosing a financial planner, it’s important to consider several factors:
- Qualifications and Credentials: Look for planners who hold certifications like CFP®, which demonstrate their expertise and adherence to industry standards.
- Compensation Structure: Understand how the planner is compensated to ensure there are no conflicts of interest.
- Services Offered: Make sure the planner provides the services you need, whether that’s creating a one-time financial plan or ongoing portfolio management.
- Experience and Specialization: Some planners specialize in specific areas, such as retirement planning or tax strategies. Ensure the planner has experience dealing with situations similar to yours.
Choosing the right financial planner is essential to ensuring that your financial plan is built on sound advice and executed effectively.
Conclusion
Financial planning is an invaluable tool for achieving financial security and meeting your life goals. Whether you choose to do it yourself or hire a professional, the key is to create a clear, actionable plan that helps you manage your money wisely. With a well-designed financial plan, you can feel confident in your ability to navigate life’s financial challenges, secure your future, and achieve the things that matter most to you.



One thought on “What Is Financial Planning? A Step-by-Step Approach to Achieving Your Goals”
Comments are closed.