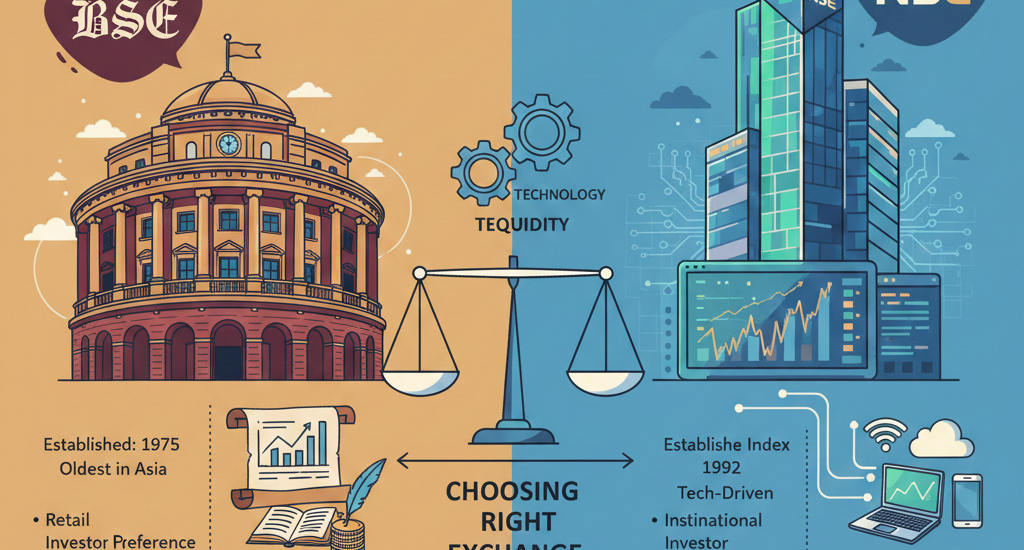
When people in India talk about the stock market, two names always appear at the top — BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange) and NSE (National Stock Exchange). Both are major stock exchanges that allow investors to buy and sell shares, but they function differently in many aspects such as history, market size, technology, liquidity, and the type of investors they attract. Understanding these differences is important, especially if you are planning to invest or trade in the Indian markets.
This article explains the key differences between BSE and NSE in a simple, human-written way, based entirely on the known structure and content of the original resource, but rewritten in an easy and comprehensive format.
1. History and Establishment
The first major difference between BSE and NSE is their age and historical background.
BSE, established in 1875, is not just India’s oldest exchange — it is the oldest stock exchange in Asia. It started as a physical marketplace under the banyan tree near Mumbai’s Town Hall where brokers gathered to trade. Over decades, it evolved into a central trading place for thousands of companies across India. Its long history gives it recognition, legacy, and trust among traditional investors.
In contrast, NSE is relatively new. It was founded in 1992 and began trading in 1994. NSE was born at a time when India was modernizing its financial markets after liberalization. It came with a clear goal — to bring transparency, technology, and nationwide access to stock trading. From day one, NSE introduced electronic trading, something that transformed how markets operate in India.
So, the key difference here is:
- BSE = Oldest, legacy-driven, historic exchange
- NSE = Modern, technology-first, fast-growing exchange
2. Benchmark Indices: Sensex vs Nifty
Every stock exchange uses an index to represent the performance of the overall market. In the case of India:
- BSE is represented by the Sensex
This index includes 30 of the largest and most stable companies across different sectors. Sensex is one of the oldest indices in the world and is widely used to measure the Indian market’s strength. - NSE is represented by the Nifty 50
This index includes 50 major companies and is considered more diversified because it covers a wider range of sectors compared to Sensex. For many traders, Nifty is the most actively followed index in India due to its liquidity.
Because Nifty includes more companies, many traders believe it gives a slightly broader view of the market, while Sensex offers a more focused, stable snapshot.
3. Number of Listed Companies
Another major point of difference lies in the number of companies listed on each exchange.
BSE has more than 7,000 listed companies, making it one of the largest exchanges globally in terms of listings. This includes large-cap, mid-cap, and significantly more small-cap and micro-cap companies.
On the other hand, NSE has around 1,600 to 1,800 listed companies. While the number is smaller, NSE hosts many of India’s biggest and most actively traded firms.
In simple terms:
- BSE = More companies, huge variety
- NSE = Fewer companies, but higher trading participation
If someone wants to explore a wide pool of stocks, especially small and mid-sized firms, BSE offers more options. However, the most active market participants, including institutional traders, tend to prefer NSE.
4. Liquidity and Trading Volume
This is where NSE stands out strongly.
NSE consistently has higher liquidity and trading volume compared to BSE. This means:
- Orders get executed faster,
- Price differences are smaller,
- Slippage is reduced,
- Traders experience smoother market operations.
For example, if a trader wants to buy or sell a large quantity of shares quickly, NSE usually handles it better due to its high number of active buyers and sellers.
While BSE also has a deep market, its trading volume is much lower, which makes it comparatively less favorable for high-frequency or high-volume traders.
This is a big reason why:
- Traders prefer NSE, especially for intraday and derivatives.
- Long-term investors use both, depending on the stock availability.
5. Technology and Trading Mechanisms
NSE has always been considered India’s technology leader in the stock market ecosystem.
- A fully automated electronic trading system
- Nationwide access to brokers and investors
- Modern risk management practices
- A robust online order-matching mechanism
Before NSE came in, much of BSE’s trading was done through an open-outcry system. Although BSE quickly adopted electronic trading after NSE’s arrival, NSE’s early head start helped it dominate the technology-driven trading landscape.
Even today, NSE’s systems are viewed as:
- Faster
- More efficient
- More reliable during high-volume sessions
However, BSE has also upgraded significantly. Its trading platform, BOLT, is fast and efficient, and BSE even launched BSE StAR MF, one of the largest mutual fund distribution platforms in India.
6. Investor Preference: Which One Is Better?
Investors and traders choose exchanges based on their goals:
BSE is preferred by:
- Investors who want access to a wider variety of stocks
- Those looking at many small-cap and mid-cap opportunities
- People who rely on long-term investing, where liquidity is not the biggest concern
NSE is preferred by:
- Active traders (intraday, derivatives, options)
- Institutions like banks, mutual funds, and foreign investors
- Anyone who needs high liquidity and fast execution
Most companies today are listed on both exchanges, so investors can pick either one to trade the same stock. But when it comes to derivatives trading, NSE has a massive edge — it handles almost all derivatives volume in India.
7. Products Offered
Both exchanges offer:
- Equity trading
- Equity derivatives
- Currency derivatives
- Commodity derivatives
- ETFs
- Bonds
- SME platforms
However, NSE dominates the derivatives segment, which is one of the most actively traded product categories in India.
Conclusion: BSE vs NSE — Which Should You Choose?
Both exchanges play a crucial role in India’s financial system, but they serve slightly different needs.
- If you want high liquidity, fast execution, and vibrant derivatives trading, the NSE is the go-to choice.
- If you want more stock variety, especially among small-cap companies, BSE offers broader listings.
- For long-term investors, both exchanges work equally well because many major companies are listed on both.
Ultimately, the best approach is to choose the exchange that supports your investing style. Most traders today prefer NSE for speed and liquidity, while many investors still appreciate BSE for its heritage and wide selection of companies.



One thought on “BSE vs NSE: Key Differences, Market Strengths, and Investor Benefits Explained”
Comments are closed.