Foreign exchange, or forex, is one of the most active and influential markets in the financial world. If you’ve ever traveled to another country, bought an imported product, or watched global financial news, you’ve already brushed against the forex market without even realizing it. Behind the scenes, currencies are constantly being exchanged, and these movements determine how much your money is worth in another country. For traders, forex also represents a massive opportunity to speculate, invest, and diversify.
This guide breaks down what forex is, how the market functions, who participates in it, and what beginners should understand before stepping in. Everything is explained in simple, human language so you can build a solid foundation.
What Exactly Is Forex?
At its core, forex is the process of converting one currency into another. It could be as simple as exchanging dollars for euros before a trip or as complex as a multinational corporation hedging millions of dollars to protect itself from fluctuations in exchange rates.
But forex trading is not limited to basic transactions. Most of the daily activity in this market—running into trillions of dollars—comes from traders who buy and sell currencies to profit from changes in price. They don’t want the actual currency in hand; they simply want to benefit from its rising or falling value.
With daily trading volumes exceeding every other financial market, forex is truly global. It has no central exchange and operates through a network of banks, institutions, and brokers spread across the world.
A Market That Never Sleeps
One of the reasons forex is so appealing is that it runs almost nonstop throughout the business week. Because trading passes from one major financial hub to another—Tokyo, London, New York, Sydney—the market remains open 24 hours a day from Monday to Friday.
This constant availability benefits traders in several ways:
- You can trade at a time that suits your lifestyle.
- News events from different regions can create opportunities around the clock.
- Market gaps are less common than in stock trading because prices continuously update.
For people with busy work schedules, forex offers flexibility that many other markets don’t.
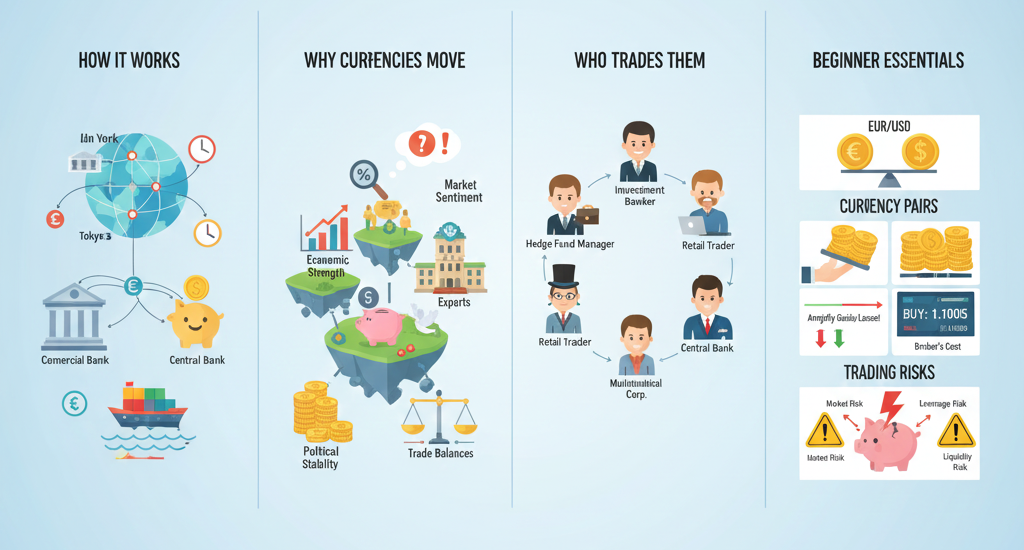
Who Actually Trades in the Forex Market?
Beginners sometimes assume forex is only for banks or large companies, but the market is filled with a wide variety of participants:
1. Major Banks
Large international banks form the core of the forex market. They handle huge volumes on behalf of clients and for their own trading desks. Their transactions help determine the real market price at any given moment.
2. Corporations
Multinational companies that do business globally need to convert currencies regularly. For example, a tech company earning in euros but paying suppliers in yen must constantly manage exchange rates.
3. Central Banks
National central banks influence their own currency through monetary policy. Interest rate decisions or direct interventions can cause major currency movements.
4. Hedge Funds and Financial Institutions
These players often trade forex to speculate or balance their portfolios, taking advantage of market volatility.
5. Retail Traders
Thanks to online brokers and trading platforms, individual traders like you now participate in the forex market with ease. Even though retail traders make up a small portion of total volume, they are active and influential in certain trading sessions.
Altogether, these participants create one of the most liquid, active, and competitive markets worldwide.
Currency Pairs: The Building Blocks of Forex Trading
Unlike stocks, which you buy individually, forex transactions always involve two currencies. These are called currency pairs. Each pair consists of:
- Quote currency – the second currency
For example, in the pair EUR/USD:
- EUR is the base currency
- USD is the quote currency
If you buy EUR/USD, you’re buying euros while simultaneously selling dollars. If you sell the pair, you’re doing the opposite.
The price displayed represents how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency. So if EUR/USD is 1.09, it means one euro equals 1.09 US dollars.
Understanding pairs is essential because forex trading is always about comparison—how one currency performs relative to another.
How Do You Actually Trade Forex?
Trading forex involves predicting whether a currency pair will rise or fall. To participate, traders generally use online platforms that provide real-time charts, analysis tools, and order execution.
Here are the key concepts beginners should understand:
1. The Spread
It serves as the main cost of trading. Lower spreads are cheaper and generally better for traders.
2. Margin
Margin is the deposit you need to open and maintain a leveraged position. You don’t pay for the full value of your trade upfront; instead, you put down a small percentage as collateral.
3. Leverage
Leverage allows you to control a large trade size with a relatively small amount of capital. For example, leverage of 1:30 lets you trade $30,000 with just $1,000 in your account.
While leverage can multiply your potential profits, it also increases your losses at the same rate. This is why understanding risk is essential for new traders.
What Makes Currencies Move?
Currency prices are influenced by a combination of economic, political, and market factors. Some of the most important include:
Interest Rates
One of the biggest drivers in forex. Higher interest rates tend to strengthen a currency because they attract foreign investment.
Economic Indicators
Reports like GDP, inflation data, unemployment figures, and manufacturing indices can all cause currency values to rise or fall.
Political Events
Elections, geopolitical tensions, trade agreements, and unexpected announcements can have immediate market impact.
Market Sentiment
Sometimes traders react based on expectations rather than facts. Speculation plays a major role in daily price movements.
The constant flow of news and data is what makes forex exciting but also unpredictable.
The Opportunities and Risks of Forex Trading
Forex offers exceptional liquidity, meaning you can enter and exit trades quickly. The market’s size and volatility create frequent opportunities for profit.
But trading also comes with risks:
- High volatility can cause rapid price swings.
- Leverage magnifies both gains and losses.
- Slippage increases costs during fast-moving markets.
Because of this, risk management tools such as stop-loss orders, limit orders, and careful position sizing are essential. Successful traders focus as much on managing risk as finding opportunities.
Final Thoughts
Forex is a fascinating market that connects every corner of the global economy. Understanding how it works—what drives price movements, how pairs are structured, what trading costs look like, and who participates—gives you a clear foundation for exploring trading with confidence.
For beginners, starting with education, practice accounts, and disciplined strategies is the smart path. With time, patience, and experience, you can decide whether forex trading fits your financial goals.